Written by
wano
on
on
Angular Fisheye Image
Angular Fisheye Image Mapping: from 3D point to pixel
ChatGPT는 angular fisheye image에 대해서 다음과 같이 설명합니다.
Angular fisheye 이미지는 광각 렌즈로 찍은 이미지로서 일반적인 렌즈에서는 담기 어려운 넓은 영역을 한 눈에 볼 수 있게끔 합니다. 이 방법은 이미지의 중앙 부분은 실제 크기와 같은 크기로 유지하면서 이미지의 외곽 부분은 중앙 부분에 비해 크게 변환되는 것을 특징으로 합니다. 이러한 변환은 이미지의 외곽 부분이 중앙에 가까울수록 크게 보이고, 더욱 멀어질수록 작게 보입니다. 이 방법은 주로 지도, 팬오버(Panoramic Overviews), 사용자 인터페이스 등에서 사용됩니다. 이 방법은 360 시각 콘텐츠를 만드는 효과적인 방법입니다. 그러나 이미지 왜곡이 있으므로 일부 상황에서는 적합하지 않을 수 있습니다.
3차원 공간상의 한 점을 angular fisheye image의 픽셀 좌표(pixel coordinate)로 변환하는 C언어 스타일의 pseudo code는 다음과 같습니다.
CPU Code (host code)
Image img; // the image rendered with a fisheye lens
img.load( "rendering_result.exr" );
// given data
Point worldCameraPosition = ...;
Point worldAimingPoint = ...;
// In this example, we assume that the up vector is the world y-axis and remains fixed.
Vector upVector = Vector( 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 );
// three orthogonal unit axes of the camera space
// xAxis: right vector
// yAxis: up vector
// zAxis: viewing direction
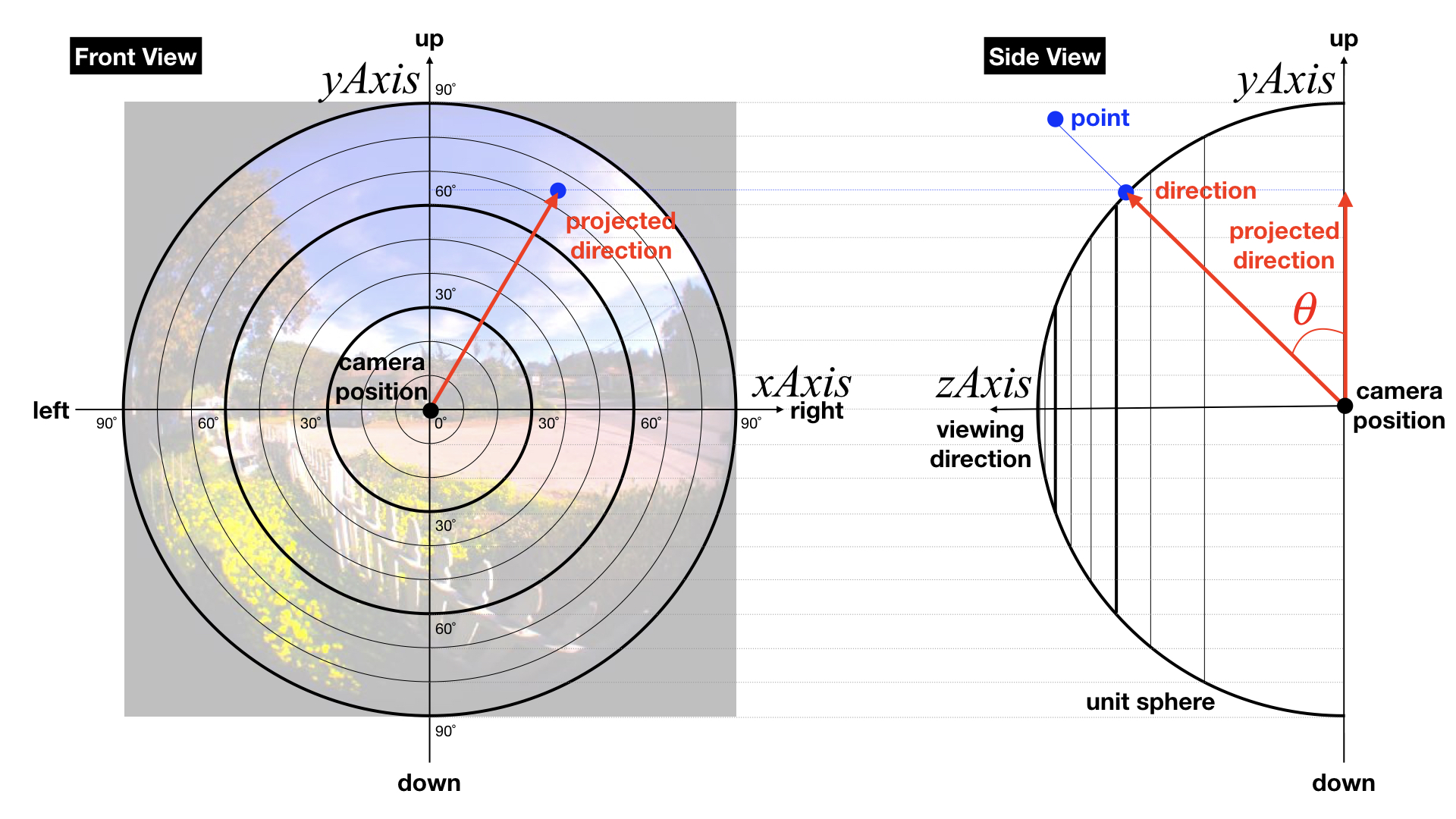
Vector zAxis = Normalize( worldAimingPoint - worldCameraPosition );
Vector xAxis = Normalize( Cross( zAxis, upVector ) );
Vector yAxis = Normalize( Cross( xAxis, zAxis ) );
Shder Code (per pixel operation)
// the wotld position of the current pixel where RGB values need to be determined
Point worldPoint = ...;
// The unit directional vector corresponding to the pixel being queried.
Vector direction = Normalize( worldPoint - worldCameraPosition );
// the coordinates of its end point
// on the xy-plane of the camera space
Real xValue = Dot( direction, xAxis );
Real yValue = Dot( direction, yAxis );
// the projected directional vector
// onto the xy-plane of the camera space
Vector projectedDirection = ( xValue * xAxis ) + ( yValue * yAxis );
// the angle between projectedDirection and direction
// cos(theta) = Length(projectedDirection) / Length(direction)
// and the denominator Length(direction) = 1.0
// direction = forward: theta = pi/2
// direction = right or left: theta = 0.0
Real theta = acos( Length( projectedDirection ) );
// Convert theta to alpha that is the scaling factor in the image space.
// the range of theta: pi/2 (forward) ~ 0.0 (right/left)
// the range of alpha: 0.0 (forward) ~ 1.0 (right/left)
Real alpha = 1.0 - theta / ( 0.5 * PI );
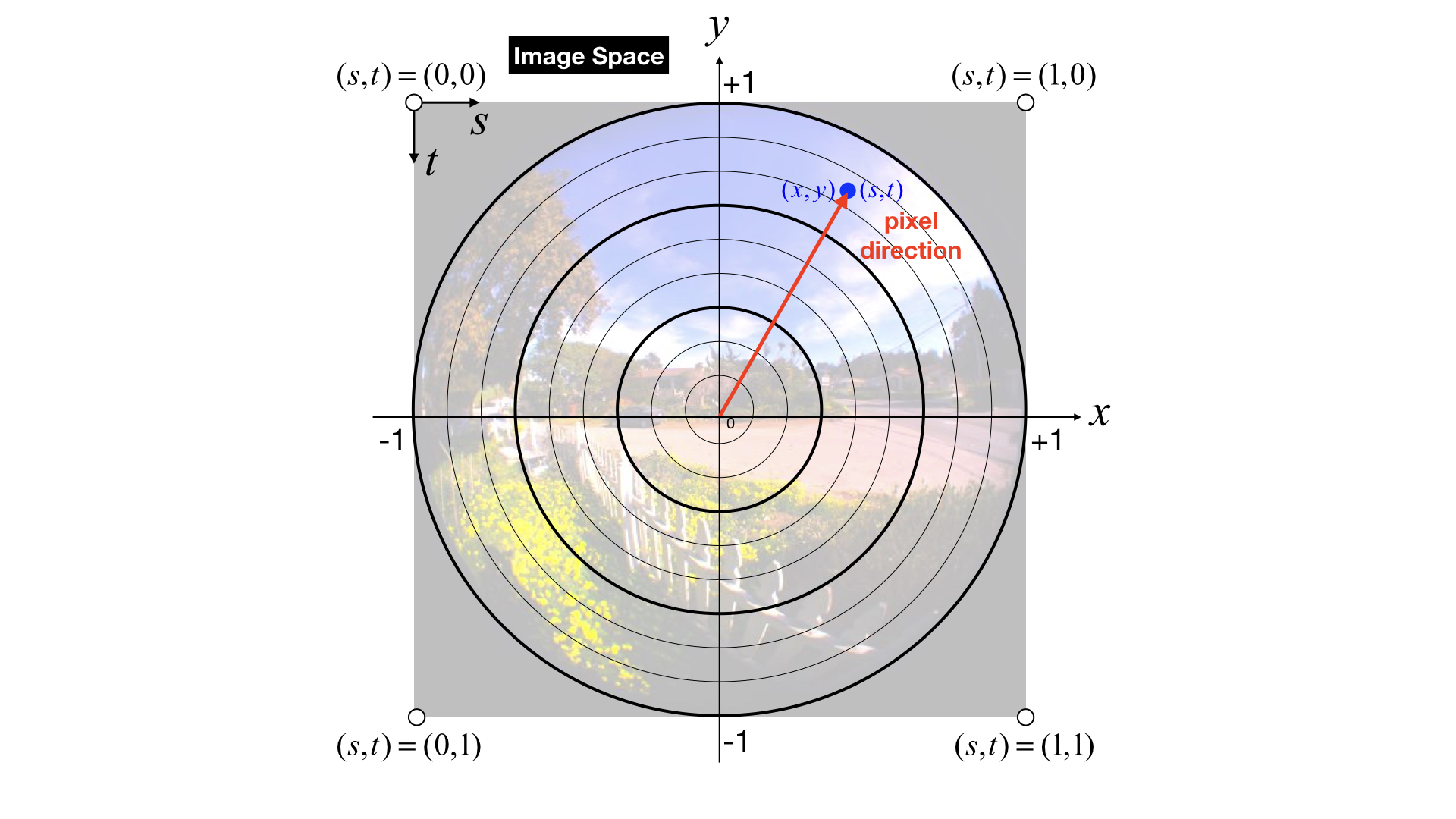
// the vector from the image center to the pixel
Vector pixelDirection = Normalize( projectedDirection ) * alpha;
// xy coordinates: -1.0 ~ +1.0
// origin: center
// x-direction: right
// y-direction: up
Real x = Dot( projectedDirection, xAxis );
Real y = Dot( projectedDirection, yAxis );
// st coordinates: 0.0 ~ 1.0
// origin: bottom-left
// s-direction: right
// t-direction: up
Real s = ( 0.5 * x ) + 0.5;
Real t = ( 0.5 * y ) + 0.5;
// Now, we are ready to get the pixel color.
// Why 1-t rather than just t?
// Because the origin of an image is the top-left corner.
Color pixelValue = img.sample( s, 1.0 - t );
return pixelValue;